Mallorca 1999 - Identification and Characteristics of Surface Components
M03 The Securitest
THE SECURITEST :
APPARATUS TO MEASURE THE INTERACTION
BETWEEN FOOT AND SPORT SURFACE
By D. Boisnard LABOSPORT

INTRODUCTION :
The aim of this new test method is to assess the friction between foot and sport surface, but also the warming up and abrasion of the skin during the friction.
This machine was built after a research in Labosport, with ANVAR funding. An improvement was done last year in collaboration of Wassing firm in Germany. The apparatus will be presented by a video tape. It records all along the test the vertical force, the speed, the horizontal force and the temperature of the skid. The vertical force is given by pressure air which involves a constant force during the test.
A coefficient of friction is then calculated.
Why we produced a new apparatus for measuring friction :
- No apparatus is suitable for synthetic turf because the distance of friction is difficult to settle (high deformation) and not accurate, because the vertical force and speed vary during the test, because the discrimination of different products is difficult and because results do not correlate to the practice.
- In the European standardization, no apparatus was proposed to determine the interaction between skin, clothes and surface.
- We need to wove the parameters : speed, vertical force and skid (dimension and quality).
- Existing apparatus are using parameters far from reality of the friction in sport. So criterions as surface rugosity or deformation are not taken into account. Apparatus must use parameters (force, speed...) as close as possible to the practice.
Example : comparative tests on PVC with the SRT pendulum.
| SECURITEST | SRT pendulum | |
| Surface without preparation | 0.50 | 112 |
| The same surface cover by a no sliding preparation | 0.75 | 110 |
The SECURITEST could give differences on different preparation of surfaces, not the SRT (RRL).
I FRICTION / TRACTION :
From the documentation we know that the Coulomb laws are not applicable with rubbers and polymers.
In 1982, Bring noticed that that the coefficient of friction is the addition of an adhesion coefficient of friction and a deformation coefficient of friction, and that the adhesion coefficient could be higher than one.
With synthetic turf and also for surfaces with high deformation, due to the texture of the product (pile height), there is a reactional force which increase the coefficient of friction measured with an apparatus :
COF = fa + fd + fr
This reactional force could mean that the real term for friction is traction (term used for the natural surfaces). Nevertheless we will adopt for the results the term of COEFFICIENT OF FRICTION, COF.
The conclusion is that COF is for polymer materials not limited to 1
Examples of SECURITEST measurements on different surfaces :
- Synthetic turf : Leisure-floor: only 5mm fibre length
- Synthetic turf : PP
- Synthetic turf : LSR3
- Synthetic turf : Nylon
- Synthetic turf : Plastic back: Floor with plastic back
- Synthetic turf : SPF
- Wood floor
- Track
Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
COF | 0.95 | 1.25 | 0.80 | 1.25 | 1.35 | 1.45 | 1.15 | 0.4 |
Sliding device : Desmopan
II DETERMINATION OF THE TEST PARAMETERS
The sliding materials:
- Crystal rubber: Synthetic transparent rubber (Polybutadien, CB), extremely good in wear (DIN: 30mg). used for transparent out-soles for Adidas shoes.
- Adidas beige: TPU-Material used for the sole of soccer-boots.
- Adidas white: TPU-Material used for the studs of soccer-boots.
- Desmopan: Thermoplastic PU but elastomer! (TPE-U), product of Bayer.
- PVC: Hard PVC (Palight S white), same material as used for securitest housing.
Comparative results : see graph 3
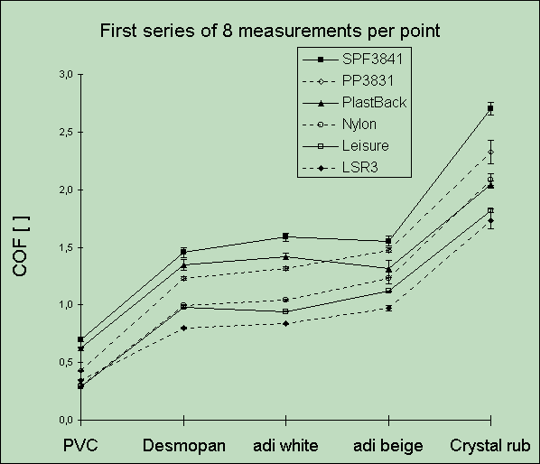
Conclusion : necessity to adapt a rubber near the quality of the shoe.
1. Pressure Variation (graph 1: x-axis is gas pressure = vertical force)
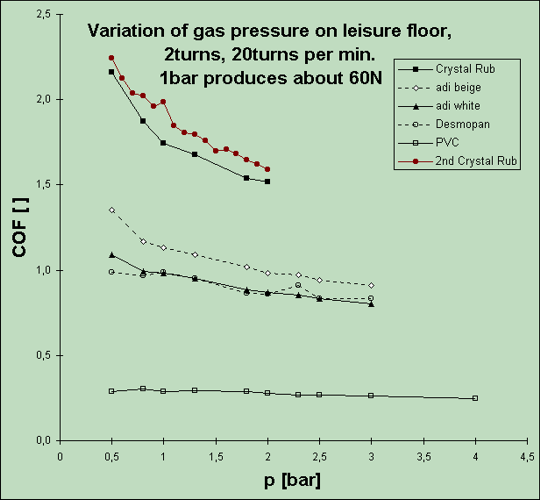
We tried out the different sliding materials on a leisure-floor.
We found a dependence (dependent on the material more or less) of COF on the pressure. The higher the pressure the lower is COF. There seems to be a saturation for higher pressures. All this corresponds to the literature (more than 80 N).
The graph 4 shows this saturation with different floors.
2. Speed variation (Graph 2 : x-axis is horizontal speed)
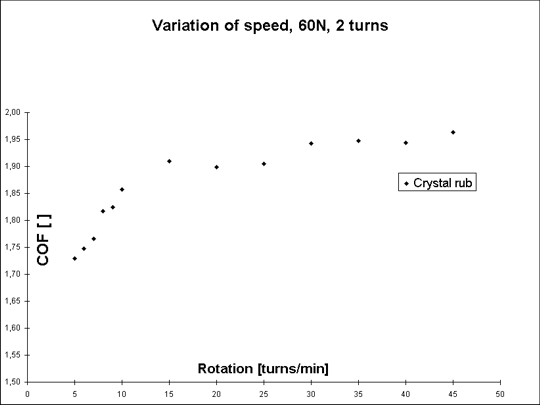
We tried out with crystal rubber all at 1bar (60N), 2 turns, 20turns/min.
We found out a strong dependence for small speeds (below 0.3 m/s). The higher the speed the higher COF with about +0.1 in COF for +0.1 m/s. For higher speeds we find a kind of a saturation (higher 0.6 m/s).
III VALIDATION OF THE SECURITEST
3. Reproducibility (Graph 3, with y-error bars that give the standard deviation of COF).
We tried out 8 times for each floor and each foot the reproducibility (all at 1bar, 2 turns, 20 turns per minute).
Conclusions :
- Very good reproducibility. Good accuracy ; nevertheless more COF increases more the error increases, so we have to choose a rubber device with a low COF.
The phenomenon of friction changes itself :
Temperature : We found a direct influence when we do not wait between two measurements. For our standard condition (2 turns, 20 turns per minute, 1 bar) we found that for the high friction Crystal Rubber a 2 minutes pause is already sufficient. If pressure, speed and numbers of turns are increased, pauses have to be longer.
Humidity : Humidity can have a big influence dependent on the materials. In the literature we found for polished steel on Polyamid 66 between 10% (COF 0.5) and 80% Humidity (COF 0.12) a monotonously declined behaviour. Other materials show no influence, e.g. polished steel on high density polyethylene. Thus the humidity has also to be controlled.
CONCLUSIONS :
General Statements :
COF is for polymer materials not limited to 1. To find higher values is not a big surprise (see e.g. standard book for friction science "Tribologie").
SECURITEST is able to classify floors in a reproducible way.
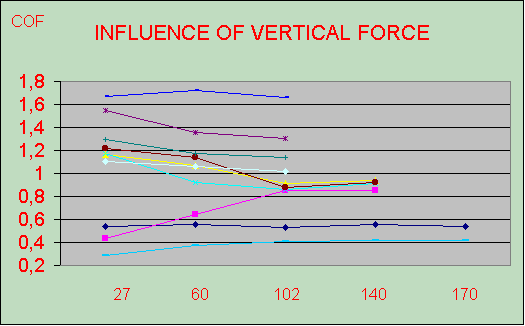
As there is a high dependence on the speed a standard should be done with a realistic speed. At least a speed should be used that is in the saturated area of e.g. higher 0.6 m/. Same is true for the dependence on the normal force. The vertical force must be adjusted more than 80 N.
The standard rubber (from SRT) is not suitable for testing on synthetic turf. The material is extremely rubbed out due to high friction. The rub-out pollutes the turf and influences further measurement. The surface structure is changed completely during an experiment (micro-waves perpendicular to moving direction).
The hardness and quality of the skid must to be the same than sport shoes.
The apparatus SECURITEST is important for research because vertical force and speed could vary, but for the tests we will take the vertical force of 80 N and the speed of 60 cm/s.
A collaboration with biomecanic organism will be important to adjust the parameters.
The apparatus SECURITEST classifies synthetic turf and other sport surfaces.
In the future we will improve the device to measure the temperature of the skid, so a sport surfaces could be classified by :
- its coefficient of friction
- its warming up during the test
- its non abrasive characteristics
In addition the apparatus could be used with different devices : ball, shoes, rollers, abrasive
Cagliari: 25 & 26 October 2018
The ISSS has successfully concluded the AGM and the Technical Conference in Cagliari. Scientific and Individual Members present accepted financials, audit report and activity schedule as presented.
Details Here
